Neck pain
Pain in the neck is common these days. About 75% of people have neck complaints at some point
Osteoarthritis is a condition that affects the joints. It commonly occurs in the hips and knees. Almost a million people in the Netherlands have osteoarthritis in these joints. Osteoarthritis is more common in older people but can also affect younger people, especially after a knee injury or joint surgery. It is a chronic and slowly progressive condition. ‘Chronic’ means that it cannot be cured. ‘Slowly progressive’ means that it gradually gets worse over time. Osteoarthritis affects different tissues in and around the joint.
This short animation explains what happens in osteoarthritis.
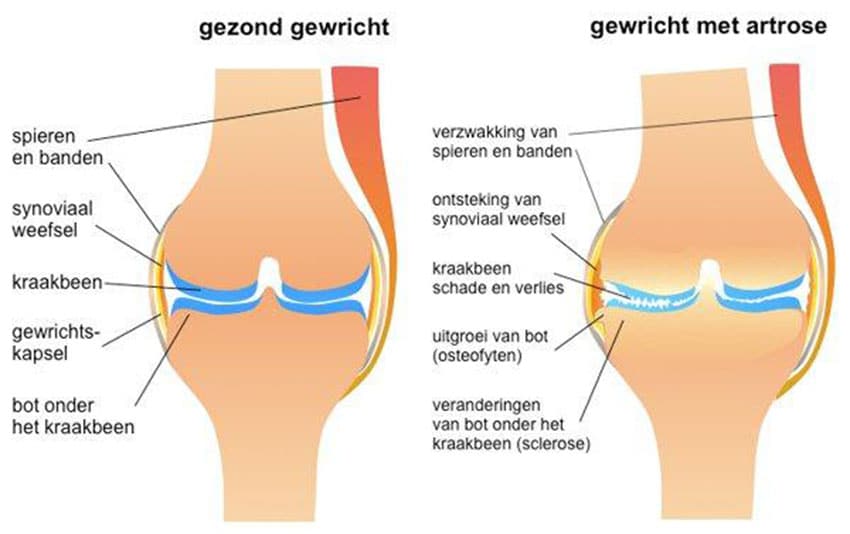
Source: The Dutch Arthritis Society (ReumaNederland)
In this picture you can see a healthy joint (on the left) and a joint with osteoarthritis (on the right). Joints work like hinges. The smooth cartilage and fluid in the joint allow the bones to move freely against each other so the joint can bend and straighten. The cartilage also acts like a shock absorber and cushions the impact on the joint. The ligaments and joint capsule serve to stabilise the joint.
Cartilage: As (the quality of) the cartilage in the joint deteriorates, the ends of the bones get closer together. The joint is then less able to absorb the impact of movement. You could think of it like a car with worn shock absorbers.
Bone: When you have osteoarthritis, it puts more stress on the bone beneath the cartilage. The bone responds to this extra stress by increasing the surface area of the joint. This causes bony growths to develop along the edges of the bones. These bony growths are known as osteophytes.
Ligaments: When there is less cartilage, it weakens the ligaments.
Muscles: People with osteoarthritis tend to move less. This weakens the muscles around the joint.
When you have osteoarthritis, the joints can become inflamed. They become swollen and feel warm to the touch. The inflammation is probably caused by loose fragments of cartilage in the joint cavity.
These changes in and around the joint can alter the alignment of the joint and may even lead to deformity of the joint. This is why osteoarthritis is also known as ‘arthrosis deformans’, which is Latin for ‘deformity of the joints’.
Despite extensive research, the cause of osteoarthritis is not completely understood. However, certain factors are known to increase the risk of osteoarthritis. These include a family history of osteoarthritis, being a woman and being overweight.
It possible to inherit an increased risk of developing osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis is more common in some families than in others. People who are genetically more likely to develop osteoarthritis typically develop it at a younger age and in several joints.
Osteoarthritis is twice to three times more common among women than men.
Other factors that increase the risk of osteoarthritis include:
Pain is often the first symptom. In some people the symptoms, such as joint pain and problems moving the joint, remain the same for a long time. Others find that their symptoms gradually get worse. Over time, osteoarthritis can result in a range of symptoms.
Osteoarthritis can be diagnosed without an X-ray. A doctor or therapist will be able to determine if your symptoms are caused by osteoarthritis. Sometimes information and advice on things you can do to ease your symptoms are not enough. Suitable treatment is needed. Your first option is to try physiotherapy. The following treatments are often helpful:
When it comes to treating osteoarthritis, physiotherapy is as effective as, and sometimes more effective than, medication and there are no unpleasant side effects. The physiotherapist who treats you will also explain and advise you on things you can do to ease your symptoms.
Treatment consists primarily of specific exercises that help improve the function of the joint. These exercises are designed to increase mobility, stability and muscle strength. This improves the body’s ability to bear weight and may alleviate the symptoms.
Our physiotherapists are available nearby to provide immediate treatment for your symptoms. We have a practice in your company or in the area, so you can start treatment straight away and do not have to spend time travelling. Our physiotherapists are familiar with your workplace. They know a great deal about the workstations, working postures, workloads and strains that the employees within the company have to deal with. They will assess your condition and determine the right treatment and guidance to best meet your needs.
At High Five we believe that a healthy mind and body are essential to living with vitality and being the best version of yourself: strong, resilient, well balanced and happy. Physiotherapy prevents, treats and relieves physical pain, improves your range of movement and helps you maintain it. Physiotherapists are experts in posture and movement.